benzodiazepine side effects, Side Effects, and Addiction
benzodiazepine side effects, and how do they work (mechanism of action)?
What are benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines are man-made medications that cause mild to severe depression of the nerves within the brain (central nervous system) and sedation (drowsiness).
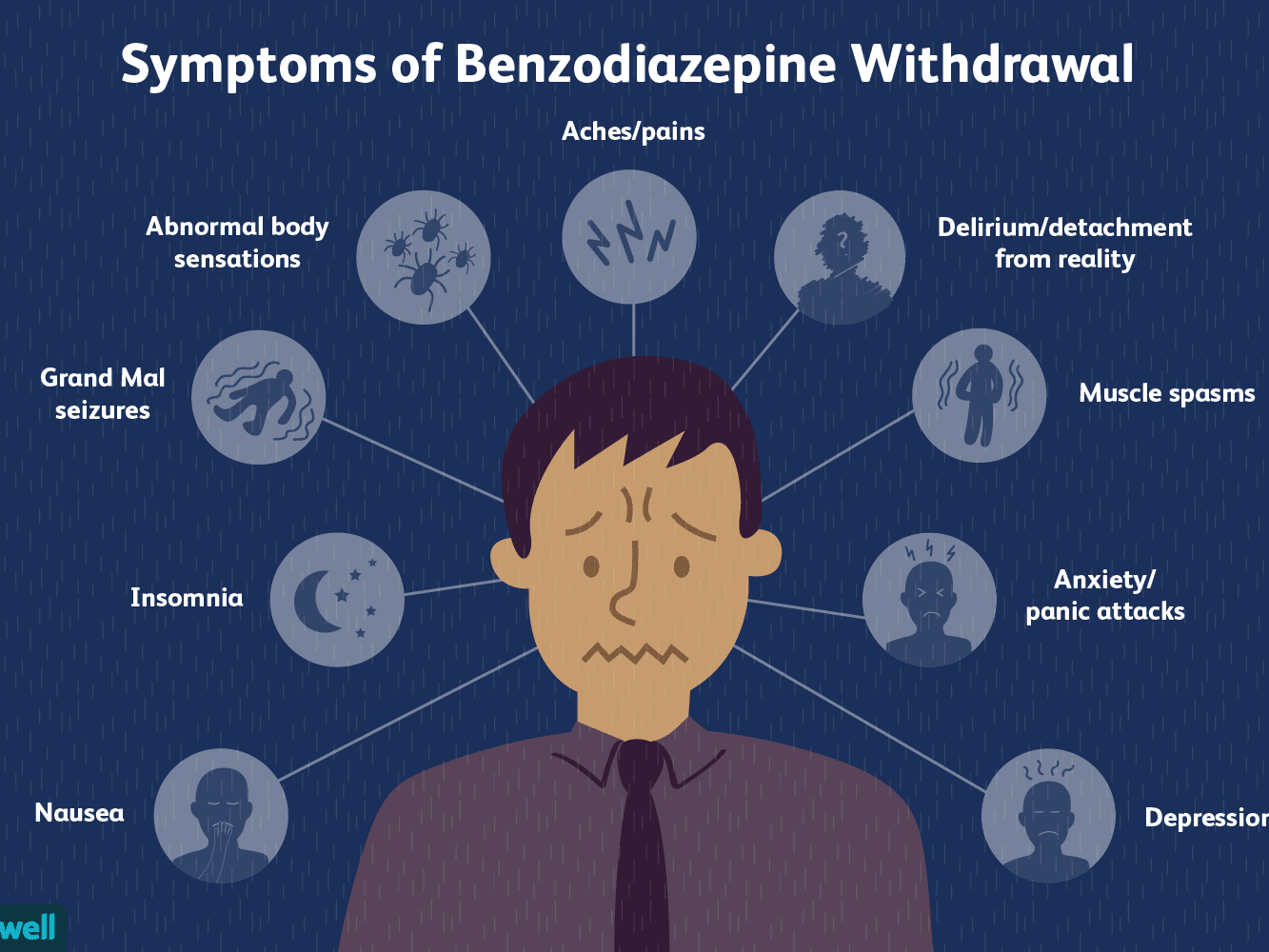
benzodiazepine side effects Seizures, anxiety, and other diseases that require benzodiazepine treatment may be caused by excessive activity of nerves in the brain. These drugs may work by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. Gamma-aminobutyric acid is a neurotransmitter, a chemical that nerves in the brain use to send messages to one another. Gamma-aminobutyric acid reduces the activity of nerves in the brain and increasing the effect of GABA with a benzodiazepine, reduces brain activity.
What are the uses for benzodiazepines?-benzodiazepine side effects
Adult men and women use benzodiazepines to treat:
Anxiety disorders are serious medical illnesses that affect approximately 19 million American adults. In fact, anxiety disorders as a group are the most common mental illness in America. Anxiety disorders can affect adults, children, and adolescents.
These disorders fill people’s lives with overwhelming anxiety and fear. Unlike the relatively mild, brief anxiety caused by a stressful event such as a business presentation or a first date, anxiety disorders are chronic, relentless, and can grow progressively worse if not treated. People who suffer from anxiety disorders typically struggle with difficult symptoms such as agitation, feeling “uptight,” worry, and apprehension on a daily basis. These disturbing symptoms can become so severe that they interfere with normal daily activities. Sometimes anxiety disorders lead to restlessness, poor sleep and insomnia, trouble concentrating, feeling tense, a sense of dread, chest pain, lightheadedness, trouble breathing, hyperventilation, and even overwhelming panic with a feeling of losing control.
Related Symptoms & Signs-benzodiazepine side effects
- What are benzodiazepines, and how do they work?
- For what conditions are benzodiazepines used?
- Are there differences between benzodiazepines?
- What are the side effects of benzodiazepines?
- With which drugs do benzodiazepines interact?
- What are some examples of benzodiazepines?
ARE THERE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN BENZODIAZEPINES?
Benzodiazepines differ in how quickly they start working, how long they continue to work, and for what they are most commonly prescribed.
- Diazepam (Valium) and clorazepate (Tranxene) have fast onsets of action and usually start working within 30 to 60 minutes.
- Oxazepam (Serax) has a slow onset, and lorazepam (Ativan), alprazolam (Xanax), and clonazepam (Klonopin) have intermediate onsets of action.
- Clorazepate (Tranxene), midazolam (Versed), and triazolam (Halcion) are short-acting agents with durations of action of 3 to 8 hours.
- Alprazolam (Xanax), lorazepam (Ativan), estazolam (Prosom), and temazepam (Restoril) are intermediate-acting agents with durations of action of 11 to 20 hours.
- Chlordiazepoxide (Librium), clonazepam (Klonopin), diazepam (Valium), flurazepam (Dalmane), and quazepam are long-acting agents with duration of action of 1 to 3 days.
- Alprazolam (Xanax), chlordiazepoxide (Librium),
- chlorazepate (Tranxene), diazepam (Valium),
- lorazepam (Ativan), and midazolam are used for anxiety disorders.
- Clonazepam (Klonopin), clorazepate (Tranxene).
- lorazepam (Ativan), clobazam (Onfi).
- and diazepam (Valium) are used for seizure disorders.
- Estazolam (Prosom), flurazepam (Dalmane), quazepam (Doral).
- temazepam (Restoril).
- and triazolam (Halcion) are used for insomnia or trouble sleeping.
- Midazolam (Versed), lorazepam (Ativan),